This post was originally published in the Daily Kos, a progressive political opinion site.

It was also reprinted under the title “Is Trump Responsible for the Violence?” on the leading corporate communication site CommPro.Biz.

by Helio Fred Garcia
The French philosopher and writer Voltaire warned that those who can make us believe absurdities can make us commit atrocities.

We have seen this phenomenon play out in all parts of the world for the nearly 300 years since Voltaire first warned us. And sadly, we see it playing out in the United States now.
I have spent nearly four decades studying leadership, language, power, and the intersection of neuroscience, anthropology, and influence. Most of my work has been in the service of helping good leaders become better leaders. But sometimes my work calls on me to send up a flare; to warn others of what I see happening and about to happen. Events of the last few weeks compel me to send up such a flare.
Genuine leaders understand the consequences of their words and actions and take responsibility when they see that they are having a dangerous impact. Self-absorbed leaders do not.
Stochastic Terrorism
There’s a phenomenon well known to those who study violent extremism and authoritarianism: the use of mass communication to inspire lone wolves to commit acts of violence. About six years ago it got the name Stochastic Terrorism, named for a principle in statistics about seemingly random things still being predictable.

Stochastic terrorism doesn’t make a direct call to violence. Rather, it leads people to take matters into their own hands. So stochastic terrorist violence is statistically predictable, even if it will not predict that a particular individual will commit a particular act against a particular person.
A Clear but Indirect Danger
The First Amendment protects free speech but not calls to violence that create a clear and present danger to people. But stochastic terrorism is insidious because it is a clear but indirect, yet still predictable, danger.
The Stochastic Terrorism Playbook
In the weeks just before the 2018 mid-term elections we saw President Trump use many elements of the stochastic terrorism playbook, that were amplified by conservative media and by Trump supporters who were running for office.
These include:
- Dehumanizing populations. This includes referring to groups of people as vermin who are infesting the country. And carrying disease – in this case including diseases that have already been eradicated or are very rare, such as smallpox and leprosy. But still scary.
- Claiming that an entire population is a threat. From his first day in the race, Trump defined Mexicans as rapists, gang members, and criminals. Candidate Trump also called for the total and complete ban of Muslims entering the country. And on his second day in office he passed an executive order, later overturned by the courts, banning people from seven primarily-Muslim countries. What the singling out of these groups, and others, have in common is that they create an Other — a group to rally against.
- Labeling an ordinary thing a serious threat. President Trump labeled a rag-tag group of impoverished men, women, and children walking north seeking asylum a Caravan. Note that seeking asylum is legal. And the people were more than a thousand miles away at the time, and on foot. Despite this, he further said that the Caravan is invading the country. Hence the very word Caravan (always capitalized) became itself a menacing word, repeated across all forms of communication — in speeches, in social media, and on television news headlines. He called the Caravan a national emergency. He also called to mobilize the military to prevent its arrival. And this wasn’t even the first time he had used the Caravan scare. He did it in April as well. That group of migrants fizzled out before most of them reached the border. Those who arrived sought asylum. We should have recognized the pattern.
- Attributing vague menacing identities to that group. For example, the claim that the Caravan has been infiltrated by a number of middle easterners.

- Saying that something is part of an evil conspiracy. In this case that the Caravan is funded by George Soros, which is white supremacist code for an international Jewish conspiracy. Note that the first bomb received in late October was sent to George Soros. Followed by an attack on a synagogue by a person driven by an urgent need to prevent Jews from bringing in refugees in order to kill Americans.
Within a single week in late October we saw tangible evidence of such rhetoric inspiring violence.
- A bomber attempted the largest assassination of political leaders in the history of the U.S., sending bombs through the mail to more than a dozen people who had each been the target of President Trump’s vitriol. Thankfully, none of the devices exploded, and all were retrieved. But authorities found the names of nearly 100 Trump critics on the bomber’s target list.
- A gunman attacked a Pittsburgh synagogue during worship, killing eleven and wounding many more. He posted online about “Jewish infestation.” In the hours before the attack, making reference to a more than century-old refugee resettlement agency, he tweeted, “HIAS likes to bring invaders that kill our people. I can’t sit by and watch my people get slaughtered. Screw your optics, I’m going in.” During the attack he yelled “All Jews must die!”
- A gunman tried to penetrate a Louisville black church but found the doors locked, and instead went into a neighboring Kroger’s store and murdered two black customers there.
There are likely to be further such acts.
Birtherism
Former First Lady Michelle Obama this week, in interviews about her forthcoming memoir, described her reaction to Donald Trump’s birther campaign, which put him on the political map for the 2016 presidential campaign. For years before and during his presidential campaign Trump persistently insisted that Barack Obama was born in Kenya, and therefore was not a legitimate president. Trump refused to acknowledge Obama’s Hawaii birth certificate, and frequently made other claims that challenged Obama’s legitimacy as president.
In her book Michelle Obama writes that this campaign was
“deliberately meant to stir up the wingnuts and kooks. What if someone with an unstable mind loaded a gun and drove to Washington? What if that person went looking for our girls? Donald Trump, with his loud and reckless innuendos, was putting my family’s safety at risk. And for this, I’d never forgive him.”
This is a vivid example of stochastic terrorism at work.
Plausible Deniability is an Essential Part of Stochastic Terrorism
The stochastic terrorist uses inflammatory rhetoric in the full expectation that it will trigger someone somewhere to act out in some way. But there is also plausible deniability built in. The stochastic terrorist can deny that he or she had anything to do with the violence that occurs. Indeed, President Trump falls back on this frequently, including in the aftermath of the bombs sent to people he had criticized. The Washington Post reported,
“Trump told reporters later that he did not think he bears blame for the alleged crimes ‘No, not at all,’ Trump said as he left the White House for a political rally in North Carolina. ‘There’s no blame, there’s no anything,’ Trump said.”
But Why Do People Believe Absurdities?
So why do people believe absurdities, which is a precursor to committing atrocities?
The Pittsburgh gunman believed deeply that Jews were importing refugees to kill “our people.” There was no evidence that Americans were being killed by refugees. But evidence didn’t matter. There was no evidence that the migrants walking north were infected with smallpox and leprosy, claims repeated frequently by conservative media. President Trump even called members of the Caravan “young, strong men” but also said that they were diseased. Why would people believe such easily refutable claims?
To answer that question we need to recognize that the rise of Donald Trump is not a cause but rather a consequence.
It is the predictable result of decades of degradation of political discourse. This degradation was facilitated by a media more interested in grabbing an audience’s attention than in covering issues. The worst part is that we should have seen it coming.
In fact, we could have seen it coming if we had known what to look for. We should have known.
Even now as the frightening reality is finally being recognized, we seem to be grappling only with the symptom of the problem — what Trump says — without recognizing that there’s a greater challenge that will continue regardless of how we address the immediate problem.
We can solve the Trump problem but still be as vulnerable to another authoritarian figure who energizes the disenfranchised, the angry, and the scared to similar effect.
Orwell Called It

In 1946 George Orwell published Politics and the English Language. That brief essay served as the nonfiction treatment for what two years later would become Orwell’s Nineteen Eighty-Four.
Most educated Americans are familiar with Nineteen Eighty-Four. This popular novel is based in a dystopian future. The nation is in a continuous state of war. The intrusive and authoritarian government keeps people uninformed, and uses political language that is intentionally misleading. So the Ministry of Peace wages war. The Ministry of Truth controls all information, news, propaganda, and art. The Ministry of Plenty rations food. Our term “Orwellian” refers to the use of language to convey the opposite of reality.

But most educated Americans are not familiar with the essay that served as the novel’s basis. Sadly, Politics and the English Language helps us understand the current state of the American body politic, and it isn’t pretty.
Says Orwell:
“In our time, political speech and writing are largely the defense of the indefensible.”
“Political language – and with variations this is true of all political parties… – is designed to make lies sound truthful and murder respectable, and to give an appearance of solidity to pure wind.”
The problem arises when politicians use language in a disingenuous way, asserting things they don’t necessarily believe and making arguments that may sound compelling but that logically don’t make sense.
“The great enemy of clear language is insincerity. When there is a gap between one’s real and one’s declared aims, one turns, as it were instinctively, to long words and exhausted idioms, like a cuttlefish squirting out ink. In our age there is no such thing as ‘keeping out of politics.’ All issues are political issues, and politics itself is a mass of lies, evasions, folly, hatred and schizophrenia. When the general atmosphere is bad, language must suffer.”
However damaging individual instances of political language, of insincere speech, or of intentionally misleading statements may be, it’s the effect of these that causes harm.
The central idea in Politics and the English Language is this:
- Political speech has the effect of reducing citizens’ critical reasoning skills….
- …This creates a self-perpetuating cycle…
- …where as people become less discerning they become more susceptible to political speech…
- …which further diminishes their critical reasoning skills…
- …and so on…
- …and so on…
- …until a fully uninformed public creates conditions for authoritarian government to thrive.
A Cause Can Become an Effect, And So On: It’s The Cycle That Matters
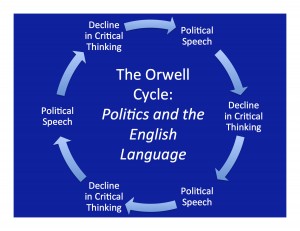 The key idea, though, is the relationship between cause and effect.
The key idea, though, is the relationship between cause and effect.
Orwell notes that an effect can become a cause, and a cause can become an effect. It’s the cycle that matters. In the end the result is a citizenry that remains intentionally ignorant of the issues that matter, unaware of what is happening to them, and easily manipulated by politicians.
“But if thought corrupts language, language can also corrupt thought. A bad usage can spread by tradition and imitation, even among people who should and do know better.”
“Now, it is clear that the decline of a language must ultimately have political and economic causes: it is not due simply to the bad influence of this or that individual writer. But an effect can become a cause, reinforcing the original cause and producing the same effect in an intensified form, and so on indefinitely. A man may take to drink because he feels himself to be a failure, and then fail all the more completely because he drinks. It is rather the same thing that is happening to the English language. It becomes ugly and inaccurate because our thoughts are foolish, but the slovenliness of our language makes it easier for us to have foolish thoughts.”
The predictable result of this cycle is a citizenry that is easily manipulated. It becomes immune to persuasion by evidence and reasoning. And it doesn’t notice the multiple contradictions all around.

Candidate Donald Trump following the Nevada primary, February 24, 2016
Choosing Ignorance: Identity-Protective Cognition Thesis
Five years ago Orwell’s argument that political language causes a decline in critical thinking was supported by research by professors at Yale, Cornell, Ohio State, and the University of Oregon. Their study, Motivated Numeracy and Enlightened Self-Government, showed that math problems that seem to be about benign topics are easily solved by people with strongly held political views. But when the same math problems are framed in terms of polarized political issues — in this case, gun rights — both progressive-and-conservative-leaning participants have a very hard time getting the math right.
The authors conclude that
“Subjects [use] their quantitative-reasoning capacity selectively to conform their interpretation of the data to the result most consistent with their political outlooks.”
A 2011 essay in Mother Jones by Chris Mooney on the neuroscience of political reasoning helps us understand why this is so. The piece begins with seminal research from the early fifties by famous Stanford psychologist Leon Festinger, who concluded:
“A man with conviction is a hard man to change. Tell him you disagree and he turns away. Show him facts or figures and he questions your sources. Appeal to logic and he fails to see your point.”
Mooney explains:
“Since Festinger’s day, an array of new discoveries in psychology and neuroscience has further demonstrated how our preexisting beliefs, far more than any new facts, can skew our thoughts and even color what we consider our most dispassionate and logical conclusions.”
“This tendency toward so-called “motivated reasoning” helps explain why we find groups so polarized over matters where the evidence is so unequivocal: climate change, vaccines, “death panels,” the birthplace and religion of the president, and much else. It would seem that expecting people to be convinced by the facts flies in the face of, you know, the facts.”
Emotion Trumps Logic
Humans are not thinking machines. We are feeling machines, who also think. We don’t think first; we feel first. What we feel determines what thinking will be possible. This is sometimes known as motivated reasoning.
As described by Chris Mooney in Mother Jones:
“The theory of motivated reasoning builds on a key insight of modern neuroscience: Reasoning is actually suffused with emotion (or what researchers often call “affect”). Not only are the two inseparable, but our positive or negative feelings about people, things, and ideas arise much more rapidly than our conscious thoughts, in a matter of milliseconds—fast enough to detect with an EEG device, but long before we’re aware of it.”
“That shouldn’t be surprising: Evolution required us to react very quickly to stimuli in our environment. It’s a “basic human survival skill,” explains political scientist Arthur Lupia of the University of Michigan. We push threatening information away; we pull friendly information close. We apply fight-or-flight reflexes not only to predators, but to data itself.”
“We’re not driven only by emotions, of course—we also reason, deliberate. But reasoning comes later, works slower—and even then, it doesn’t take place in an emotional vacuum. Rather, our quick-fire emotions can set us on a course of thinking that’s highly biased, especially on topics we care a great deal about.”
“We have seen this trend for several decades, where for political expediency citizens have been conditioned to not trust any source of news that includes conclusions contrary to those consistent with a political point of view.”
This is likely to be intensified when the news media is seen to be both purveyors of fake news and enemies of the people, two themes President Trump continuously emphasizes. This results in his followers choosing not to believe anything written in such media.
We Apply Fight-or-Flight Reflexes Not Only to Predators, But to Data Itself
Such citizens, who reflexively flee from the facts, are unlikely to be aware of, or even care about, contradictions. Simultaneously holding two contrary positions, the very definition of absurdity, would ordinarily dismiss someone as not to be taken seriously. But in the political world such contradictions seem not to matter.
In such an environment citizens literally are unable to notice absurdities. But the same part of the brain, the Amygdala, that causes the flight response also causes the fight response. So any intruder is seen to be worthy of a fight. And violence tends to ensue.
Within a week of Trump calling for a ban of all Muslims entering the country we saw a rash of attacks on mosques and on people perceived to be Muslim or Arab. We have seen people removed from his rallies while being taunted by Trump from the podium, calling for his supporters to punch the person being removed in the face. In the aftermath of the white supremacist rally in Charlottesville in August, 2017, which President Trump refused to condemn, we saw dis-inhibition in the workplace. People who previously would have kept their racist or anti-immigrant or anti-Semitic opinions to themselves felt emboldened to act out, treating colleagues and customers with insult, rudeness, exclusion, and even violence.
The New York Times reported last month,
“The hate in the United States came into full view last year as white supremacists marched in Charlottesville, Va., with lines of men carrying torches and chanting, “Jews will not replace us.” Swastikas and other anti-Semitic graffiti have been cropping up on synagogues and Jewish homes around the country. Jews online are subjected to vicious slurs and threats. Many synagogues and Jewish day schools have been amping up security measures.
The Anti-Defamation League logged a 57 percent rise in anti-Semitic incidents in the United States in 2017, compared to the previous year — including bomb threats, assaults, vandalism, and anti-Semitic posters and literature found on college campuses.
Are the Calls to Violence Intentional or Merely Reckless?
Plausible deniability is built into the dehumanizing of groups, making it difficult to draw a clear line between a particular act of speech and a particular act of violence. Some, including the president’s allies, could conclude that President Trump is not making such statements with the intention of people committing violence. Rather, he’s speaking his mind and cannot be held accountable if some crazy person takes matters into his own hands.
Contrast today with 10 years ago. Late in his 2008 run for president Senator John McCain saw the crowd crying for blood, and was admonished by people he respected about the likely effect of his rhetoric. He took those admonitions seriously, and he dialed it down. As a responsible leader does.

The book Game Change: Obama and the Clintons, McCain and Palin, and the Race of a Lifetime, by John Heilmann and Mark Halperin, describes Senator McCain’s moment of awakening. Senator McCain and his running mate, Alaska Governor Sarah Palin, had used harsh language to de-legitimize Senator Obama. Governor Palin persistently declared that Obama “palled around with terrorists.”
Game Change reports:
“As the election barreled toward its conclusion, something dark and frightening was unleashed, freed in part by the words of the McCains and Palin. At rallies across the country, there were jagged outbursts of rage and accusations of sedition hurled at Obama. In Pennsylvania and New Mexico, McCain audience members were captured on video and audio calling the Democrat a “terrorist.” In Wisconsin, Obama was reviled as a “hooligan” and a “socialist.
With the brutish dynamic apparently on the verge of hurtling out of control, a chagrined McCain attempted to rein it in. In Minnesota, when a man in the crowd said he would be afraid to raise a child in America if Obama were elected, McCain responded, “He is a decent person and not a person you have to be scared of as president.” A few minutes later, he refuted a woman who called Obama “an Arab.”

Senator McCain heard from two of his heroes: civil rights legend Congressman John Lewis, and life-long Republican and former Joint Chiefs Chair and Secretary of State Colin Powell.
Game Change reports:
McCain’s efforts to tamp down the furies were valorous, though they did nothing to erase his role in triggering the reaction in the first place. The civil rights hero John Lewis, whom McCain admired enormously, compared the Republican nominee and his running mate to George Wallace and said they were “playing with fire.”

Civil Rights Legend, Representative John Lewis (D-GA)
Another prominent African American was watching with alarm. Colin Powell had been friends with McCain for twenty-five years. The senator had been actively seeking his endorsement (as had Obama) for nearly two years. Powell warned McCain that his greatest reservation was the intolerant tone that seemed to be overtaking the Republican Party. McCain’s selection of Palin bothered Powell because he saw her as polarizing. He was dismayed by Mc-Cain’s deployment of Ayers as an issue, perceived it as pandering to the right.
And then there were the hate-soaked rallies, which he considered anti-American. This isn’t what we’re supposed to be, he thought.
Powell had leaned toward staying neutral, but these outbursts were all too much—and McCain had moved only belatedly to stop them. Obama, by contrast, had displayed terrific judgment during the financial crisis, Powell thought. And his campaign had been run with military precision; the show of overwhelming force struck the general as a political realization of the Powell Doctrine. On October 19, he endorsed Obama on Meet the Press.

Colin Powell endorses Senator Barack Obama on Meet The Press
The general’s repudiation was a stinging blow for McCain. Beyond their longtime friendship, Powell represented the same brand of Republicanism as McCain’s. Tough on defense. Fiscally prudent. Pragmatic and nondoctrinaire. McCain had to wonder what had become of him if his current incarnation was repelling someone like Powell. He was startled by the crazies at his rallies. Who were they? Why were they there? And what did they see in him? In the final two weeks of the race, McCain began to try to salvage something of his reputation.
He put away the harshest of the personal invective against Obama and went back to talking about the economy, rash spending, and Iraq.”
Leaders Choose Responsibility
Senator McCain saw the unintended consequences of his fiery rhetoric and stopped. As a responsible leader does. Leaders choose responsibility, even if there is not a direct line between what they say and the violence or threatened violence that ensues.
There are two possible conclusions about President Trump’s incitement of violence. Either it is intentional or it is reckless. Either he wants the violence, or he doesn’t care about the violence. Neither absolves him of responsibility. Indeed, it may be even more frightening if the violence is not his intention, but that he is indifferent about it.
The poet TS Eliot gave us a way to understand this.

TS Eliot
He said,
“Half the harm that is done in this world is due to people who want to feel important. They don’t mean to do harm; but the harm does not interest them. Or they do not see it, or they justify it because they are absorbed in the endless struggle to think well of themselves.”
But whether intentional or merely the result of indifference, the victims of violence experience it as real. And an effective leader would stop.
# # #
Please note: Helio Fred Garcia is executive director of Logos Institute for Crisis Management and Executive Leadership and is on the adjunct faculties of both New York University and Columbia University where he teaches, among other things, ethics. But the views expressed here are solely his own and not necessarily reflective of any other entity.